Search results: 2677
Explain the nature of finance and its interaction with other management functions
Focus on shareholders' wealth creation
Discuss agency problems
Analyze and evaluate all investments and take decisions
This Module equips students with the abilities to apply management practices in various functions of the business such as Human resources management, sales and marketing strategies, research and development, production and operations, procurement management, general administration procedures and IT aspects of the business organization.
1. Module Code: BIT 3231 School: Business
2. Module Title: Business Intelligence and Innovations
3. Year3 Trimester 2
4. Credits: 15
5. Administering School: School of Business
6. Department: Business Information Technology
7. Year of Presentation: 2018-2019
8. Pre-requisite or co-requisite modules: N/A
9. Allocation of study and teaching hours
|
|
Student Hours |
Staff hours |
|
Lectures |
60 |
55 |
|
Seminars/Workshops |
10 |
10 |
|
Practical classes/laboratory |
50 |
35 |
|
Structured exercises |
20 |
15 |
|
Set reading etc. |
20 |
15 |
|
Self-directed study |
20 |
10 |
|
Assignments – preparation and writing |
10 |
5 |
|
Examination – revision and attendance |
10 |
5 |
|
Total hours |
150 |
100 |
10. Description
This module will offer to the students with opportunity to gain an enhanced understanding of business analytics and how they do help in decision making. Understand the importance of knowledge as an intellectual asset for the organization and how it is used for value creation
11. Learning outcomes
11.1 Knowledge & Understanding: Successful completion of this module will enhance the student's ability to:
a. Define all possible tools used in current business organization for business intelligence and analytics
b. Master processes for knowledge creation and sharing in organizations
c. Understand the utility of data mining in business
d. Be able to understand to importance of innovative ideas in business
11.2 Cognitive/Intellectual skills/application of knowledge: Successful completion of this course will enhance the student's ability to:
- Identify appropriate business intelligent tools
- Explain relevant data mining techniques
to use the systems development lifecycle to build or acquire business computing
11.3 General transferable skills : Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to:
a. Explain data mining concepts
b. Explain processes of Designing the data storage using data warehousing techniques
c. Interpret the results using Knowledge management theories
d. Deciding according the information got and quickly responding to the market
e. Forecasting the market and be a forerunner on the field
12. Indicative content
Unit1: Business Intelligence
I. Introduction to Business Intelligence
A Framework for Business Intelligence (key definitions)
Transaction Processing versus Analytic Processing
Successful BI Implementation
Major Tools and Techniques of BI
II. Data Warehousing
Definitions and concepts
Data warehousing Process overview
Data warehousing architectures
Data warehouse Development
Data warehousing Implementation Issues
Real Time data warehousing
Data warehouse administration, Security Issues and future Trends
III. Data Mining for Business Intelligence
Introduction/Historical Perspective,
Fundamental concepts, Overview of data mining
Expanding universe of data Production factor
Knowledge discovery process
Data pre-processing - Measurement and Data
Visualizing and Exploring data
Data Analysis and Uncertainty - algorithms
Data Cube – OLAP – Technology
Classification and Prediction, Regression
Cluster Analysis – Mining Frequent Pattern Association -
Visualization Technique - k nearest neighbor – Decision trees – Association rules – Neural Networks – Genetic Algorithms – Reporting - Commercial data mining software applications
Text and Web Mining
Unit II: Knowledge Management & Business Innovations
Introduction – concepts and Theories
KM Technologies and Strategies
Knowledge Sharing
Community of Practices
Knowledge Applications
Knowledge systems
Knowledge Management Cycle
Business Innovations
Managing Technological Transitions
Competing in Technology Intensive Industries
Creating and Managing Innovative Organization
Applying the Ideas
13. Learning & Teaching Strategy
Development of the learning outcomes is promoted through the following teaching and learning methods:
a. Lectures are used throughout the program in order to impart essential knowledge relating to above aims and outcomes.
b. Emphasis is given on Practical oriented Approach by giving more exercises in lab, field visits and seminars
c. Student centered approach is taken whereby students are expected to do lot of exercises by taking real life examples.
d. Independent study is necessary to both assimilate and further clarification material obtained from lectures, preparation for seminars, preparation for written assessments, and the broader development of knowledge of the field of study.
e. Group work is an important part of some modules in the program and it provides an opportunity for teamwork participation, the development of interpersonal skills and the reconciliation of different points of view.
14. Assessment
The main principles underlying assessment are that understanding, interpretation and application are the crucial issues.
|
S.No |
Type of Assessment |
Learning objectives covered |
|
1 |
In-course Assessment (50%) |
All the mentioned above in section 11.1, 11.2 |
|
2 |
Final Exam (50%) |
All mentioned in 11 |
Assessment Strategy
The Assessment can take many forms such as group discussions, Assignments, Quizzes, objective questions, Continuous Assessment Tests, Practical Exercises, Presentations, to name a few. The Assessment differs from Module to module and is dependent on the module and its learning outcomes. The Module team headed by the Module Leader, come together and prepare a Module Handbook detailing the module, its learning outcomes, indicative content, the type of Assessments and its weightage, before the start of the module.
15. Indicative Resources
A. Reference Books:
Core texts:
1. Efraim T.,Ramesh S.,Darsum D.,David K.,(2011). Business Intelligence. A Managerial Approach. 2nd Ed.,Pearson, 312 p
2. Dalkir K.,(2011). Knowledge Management in Theory and Practice. 2nd Ed.,MIT, 485p
3. J. Hass and M. Kamber (2006) Data Mining Concepts and techniques, Morgan Kauffman Publishers, Elsevier Inc
4. Paulraj Ponniah (2001) Data Warehousing Fundamentals: A Comprehensive Guide For IT Professionals, Wiley Interscience Publications
5. D. J. Hand, Heikki Mannila, Padhraic Smyth (2001) Principles of Data Mining, MIT
Background texts:
6. Herwig Rollett (2003), Knowledge Management Process and Technologies, Kluwer Academic Publishers
7. Ronald Maier (2004), Information and Communication Technologies for Knowledge Management,Springer Verlak, Newyork
8. Jean-Philippe Deschamps (2008) Innovation Leaders: How Senior Executives Stimulate, Steer and Sustain Innovation, John Wiley & Sons Publishers
9. Pieter Adriana’s, Dolf Zantinge (1998) Data Mining, Addison Wesley.
10. Alex Berson and Stephen J. Smith (2004), Data Warehousing, Data Mining, & OLAP, McGraw- Hill
11. Krogh, G. and Roos, J. (Eds) (1996) Managing Knowledge: Perspectives on Cooperation and Competition. Sage, London
16. Teaching Team
Mr. PAVALAM S.M.
Mr. MUGABE Nzarama Gabriel
Unit Approval
Dean of Faculty and the Head of department implementing the program to confirm agreement
|
Unit |
Names /Designation |
Signature |
Date |
|
Business Information Technology |
Ms. S.M. Pavalam; HOD |
............................. |
............................. |
|
School of Business |
Dr. Jonas Barayandema, Acting Dean |
............................. |
............................. |
|
College of Business And Economics |
Dr. Gasheja Faustin Principal |
……………………… |
…………………… |
|
Teaching and Learning Enhancement
|
Dr. Niragire Francois, Acting Director
|
…………………….. |
…………………… |
|
Library
|
Acting Director
|
……………………….. |
…………………. |
|
ICT |
Director |
…………………….. |
……………………. |
This module introduces students to know the mode reasoning of mathematics that consists of using numbers in daily life.
The purpose of this module is to explore integrative and holistic concepts in nursing. Emphasis will be on caring and healing relationships that advance the health and well being of patients, families and systems. Caring theories for patients suffering from acute, chronic, and mental illness including life-threatening and end-of-life issues.Concepts of caring and holism are explored. Learners are expected to utilize advanced principles of communication and self-exploration throughout the module to explore personal conceptual frameworks of holism as related to healthcare in the Rwandan context.
In this module, students will be introduced to historical background of eco-physiology and the destruction of tropical forests. This module will provide a more understanding on different types of tropical forests, their physiognomy and functional structure. Furthermore, it will provide more understanding of environment factors in tropical forests (temperature, light, water, mineral nutrients). It will mainly focus on eco-physiological responses to temperature, light and to drought.
Welcome to this course of Parasitology
The aim of this module is to provide the student a general background in parasitology, the study of organisms (parasites) that live on or in other organisms (the host). The module will familiarize students with the life cycles of protozoans and parasitic helminths of major importance in Africa; it will also include their physiology and morphological adaptations, and will help understand their economic and medical importance.
Learning outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to;
1.Understand fundamental concepts and principles of parasitism, classification, ecology, morphology, lifecycle, transmission, diagnosis, prophylaxis, treatment of parasites.
2. Identify the people who are infected and types of infesting parasites based on observed symptoms
3. Prepare a protocol of parasitological study and isolate some types of parasites in
infected blood or faecal samples in laboratory
4. Apply knowledge of parasitology on one’s life and learn more with the experience of parasites known in the surrounding
This module aims to provide an integrated background in parasitology. The module will familiarize students with the life cycles of parasitic protozoans, helminths, and arthropods of major importance in Africa. At the end of this course, students must be able to explain the biology, and morphological adaptations of parasites, and understand the economic and medical importance of parasites.
This module looks at how strategy is currently practiced in a wide
variety of contexts from commercial and entrepreneurial to social and
not-for-profit. The curriculum encourages exploration of and a critical
approach to the key concepts that underpin strategic management and the
tools managers use to analyze their environment, frame choices and put
the resulting strategies into action. The programme also emphasizes the need for an holistic
perspective of the strategic issues confronting the organization and of
the performance implications of the alternative structures and processes
available for implementing strategy.
Brief description of aims
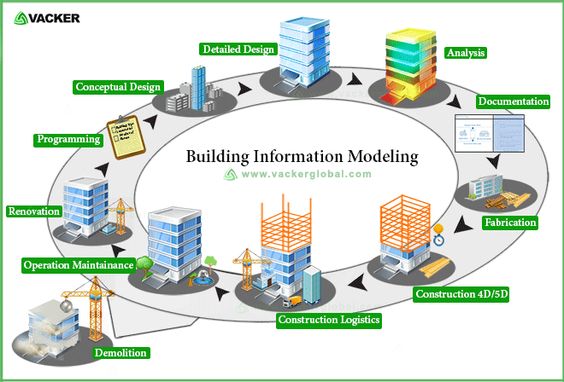
This course covers Building Information Modeling (BIM), including its use and application for small and large-scale building construction projects. Students will learn terminology associated with buildings, the theory and evolution of BIM, and how to develop BIM models using Autodesk Revit.
This course will also cover selected topics on how BIM is used to help prepare or feed into key project items, such as cost estimation, structural, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing) architectural renderings, interfererence checking, and modeling of energy consumption.
This module “Civil Engineering Project Planning & Management” is a practical, step-by-step guide to project management for Civil engineers. This module describes the techniques and strategies for creating a successful civil engineering project. It introduces civil engineering projects and their management, and then proceeds stage-by-stage through the engineering life-cycle project, from requirements, and implementation, to phase-out. It offers information for understanding the needs of the end-user of a product and other stakeholders associated with a project and is full of techniques based on real, hands-on management of engineering projects. It will equip students with the skills, aptitudes, and knowledge required of project management professionals. It will teach a core set of project skills known as the ten project management knowledge areas, including managing project integration, scope, time, cost, quality, risk, resources, communication, procurement, and stakeholders as well as a solid understanding of the key factors that impact on project success and project management success, and the relations between project management and change management. It will make students aware of the issues in identifying and selecting projects and in planning, performing, and controlling the project, with much emphasis on civil engineering projects. Whilst drawing on project management theory, the module is focused on training students in practical skills based on the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), an international standard published by the Project Management Institute (PMI).
NOTICE: This is a compulsory module for students who did CCNA version 6.
CCNAv7 Bridging provides the new topics for students who have completed CCNA R&S version 6.0 courses and want to prepare for the new CCNA certification exam (200-301). These topics were extracted from the CCNAv7: Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials andthe CCNAv7: Enterprise Networking, Security and Automation (ENSA) course.
By the end of this course, students will be able:
- Configure WLANs using a WLC and L2 security best practices.
- Explain how vulnerabilities, threats, and exploits can be mitigated to enhance network security.
- Explain how VPNs and IPsec secure site-to-site and remote access connectivity.
- Explain how network automation is enabled through RESTful APIs and configuration management tools.
The content from this course can be integrated as needed into Cisco CCNAv7 curriculum. The course includes activities using Packet Tracer, hands-on lab work, and a wide array of assessment types and tools.
CCNAv7: Introduction to Networks (ITN) covers the architecture, structure, functions and components of the Internet and other computer networks. Students achieve a basic understanding of how networks operate and how to build simple local area networks (LAN), perform basic configurations for routers and switches, and implement Internet Protocol (IP).
By the end of the course, students will be able to:
- Configure switches and end devices to provide access to local and remote network resources.
- Explain how physical and data link layer protocols support the operation of Ethernet in a switched network.
- Configure routers to enable end-to-end connectivity between remote devices.
- Create IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes and verify network connectivity between devices.
- Explain how the upper layers of the OSI model support network applications.
- Configure a small network with security best practices.
- Troubleshoot connectivity in a small network.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Alignment
Text Colour